Contribution participating in the INPST 2018 Science Communication Awards contest.

Research discoveries at Baylor College of Medicine can potentially reach the point where they evolve into practical applications that improve the quality of life. After more than 20 years of research, discoveries of Dr. Mary Estes’ lab have reached that point; they successfully resulted in a vaccine against rotavirus, triggered the interest of an industry partner, ImmuCell, and were ultimately developed into a final product that has been approved and is available for use in the U.S.

“When we started this research many years ago we were not planning on developing a vaccine; we wanted to understand the structure and biology of rotavirus,” said Dr. Mary Estes, Cullen Foundation Endowed Professor Chair of Human and Molecular Virology in molecular virology and microbiology at Baylor College of Medicine and emeritus founding director of the Texas Medical Center Digestive Diseases Center. “Rotaviruses are the main cause of gastroenteritis in infants and children around the world; they cause more than 200,000 deaths annually.”
Years of basic research opened a number of unforeseen possibilities. The research generated not only a better understanding of the viral proteins and the capsid structure and new basic science questions, but also resulted in a candidate viral vaccine product, virus-like particles.
Their initial results were published by Dr. Sue Crawford and their collaborative team in the Journal of Virology in 1994. Many collaborators at Baylor and other institutions were involved in demonstrating that rotavirus virus-like particles are candidate vaccines for animals and humans. Key individuals included Dr. Margaret E. Conner, Dr. Sarah E. Blutt, Dr. Sue E. Crawford, and Dr. Max Ciarlet at Baylor, and Dr. Linda Saif at the Ohio State University in the Food and Animal Health Research Program.
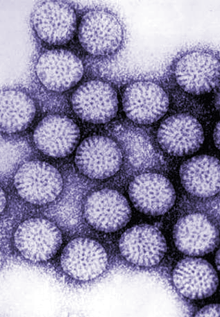
We wanted to study the subunits that form the virus so we tried a number of systems to produce the capsid proteins. We were delighted when we used the baculovirus expression system and the produced proteins self-assembled into virus-like particles,” said Estes, who also is a member of the Dan L Duncan Comprehensive Cancer Center and holds a joint appointment in medicine–gastroenterology and hepatology at Baylor College of Medicine.
“We used the particles for many basic science experiments initially and then we worked on a program for developing them as a virus-like particle vaccine. Over a number of years, we determined the best immunization protocols, including the best route and use of different adjuvants, for virus-like particles to be highly immunogenic in a number of species. Our studies showed that these particles had clear potential as a vaccine for both humans and animals.”
Although currently there are other rotavirus vaccines available, their efficacy is limited. In developed countries the efficacy is about 90 percent, but in developing countries it drops to nearly 50 percent. There is still a need for alternative immunization protocols.
The road to commercialization
The virus-like particles captured the interest of ImmuCell Corp., a growing animal health company that develops, manufactures and markets scientifically-proven products to improve health and productivity in the dairy and beef industries. One of ImmuCell’s product lines aims at preventing pathogen-caused diarrhea, or scours, in newborn calves, a significant problem in these industries.
Rotaviruses, together with other pathogens such as coronaviruses and E. coli bacteria, are the most common causes of neonatal diarrhea in calves. This condition can be fatal from the loss of nutrients and dehydration. Survivors suffer the consequences of their neonatal condition through life; they are more susceptible to disease, gain less weight and produce less milk than calves that did not have scours.
ImmuCell licensed our technology and over several years developed a product that would protect newborn calves from diarrhea-causing rotavirus,” Estes said.
The scientists at ImmuCell developed and field tested a vaccine of virus-like particles in cows. The cows responded to the vaccine by producing anti-rotavirus antibodies in the colostrum, which were tested for their ability to protect newborn cows from the virus. Successful field trials led to First Defense® Tri-Shield™, a new product that combines the anti-E. coli and anti-coronavirus antibodies in ImmuCell’s product First Defense® with anti-rotavirus antibodies.
In natural conditions, antibodies passed from the vaccinated dam to the calf through colostrum protect newborn calves from these pathogens. However, research suggests that many dams do not make sufficient levels of antibodies through this natural process so a significant number of calves remains unprotected. The new product claims to overcome this situation by directly providing calves the amount of antibodies needed to confer protection against the pathogens in a large edible capsule.
“This is a very important achievement by our development and manufacturing teams after many years of challenging work,” commented Michael F. Brigham, president and CEO of ImmuCell. “Generating a consistent level of rotavirus antibodies through our proprietary hyper-immunization program is not easy. Our prior initiatives to achieve this result did not utilize the novel technology that we have exclusively licensed from Baylor College of Medicine in Houston.”
“We state in our grant proposals that our research is to help prevent or treat disease, but it is not very often that someone successfully achieves that goal,” Estes said. “I am delighted that we have a rotavirus vaccine that has been licensed and we hope will help improve the health of farm animals. I also hope that after the success in the cattle industry, health care officials will be encouraged to think about rotavirus vaccines based on virus-like particles for children.”

We were very pleased to learn that ImmuCell has succeeded with their efforts to develop a new First Defense® product that incorporates anti-rotavirus antibodies. This is precisely the outcome that we want to see; new products introduced to the market that incorporate important discoveries from the labs at Baylor”, stated Michael Dilling, director of the Baylor Licensing Group.
At Baylor College of Medicine, the Baylor Licensing Group works with researchers to facilitate the transition from the labs to commercialization and maximize the impact of their research through commercial relationships that lead to agreements to support the development of new products and services that benefit patients and the public.
This blog post was previously published at: https://bit.ly/2SIMd0B
Keywords: Baylor College of Medicine, ImmuCell, From the Labs to Commercialization, rotavirus vaccines, molecular virology and microbiology, vaccine against rotavirus.
Join for free INPST as a member
The International Natural Product Sciences Taskforce (INPST) maintains up-to-date lists with conferences, grants and funding opportunities, jobs and open positions, and journal special issues with relevance for the area of phytochemistry and food chemistry, pharmacology, pharmacognosy research, and natural product science.