Abstract:
Introduction: The aim of the study was to undertake a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies to determine the effect of magnesium (Mg) supplementation on C-reactive protein (CRP). Design: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials (RCTs).
Material and methods: Data sources: PubMed-Medline, Web of Science, Co-chrane Database, and Google Scholar databases were searched (up until December 2016). Eligibility criteria: Randomized controlled trials evaluating the impact of Mg supplementation on CRP. We used random effects models meta-analysis for quantitative data synthesis. For sensitivity analysis was used the leave-one-out method. Heterogeneity was quantitatively assessed using the I 2 index. Main outcome: Level of CRP after Mg supplementation.
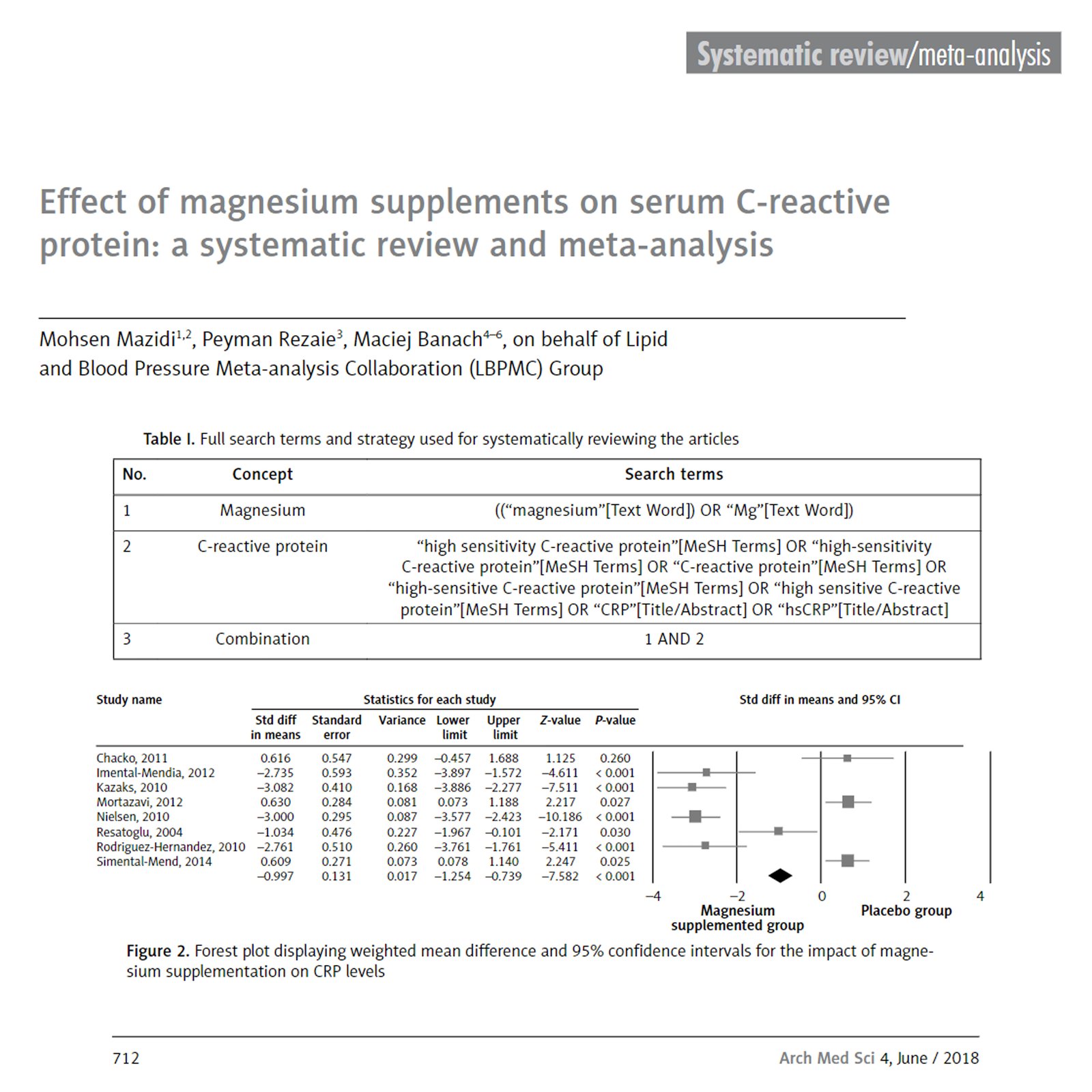
Results: From a total of 96 entries identified via searches, eight studies were included in the final selection. The meta-analysis indicated a significant reduction in serum CRP concentrations following Mg supplementation (weighted mean difference (WMD)-1.33 mg/l; 95% CI:-2.63 to-0.02, het-erogeneity p < 0.123; I 2 = 29.1%). The WMD for interleukin 6 was-0.16 pg/dl (95% CI:-3.52 to 3.26, heterogeneity p = 0.802; I 2 = 2.3%), and 0.61 mg/dl (95% CI:-2.72 to 1.48, p = 0.182, heterogeneity p = 0.742; I 2 = 6.1%) for fasting blood glucose. These findings were robust in sensitivity analyses. Random-effects meta-regression revealed that changes in serum CRP levels were independent of the dosage of Mg supplementation (slope:-0.004; 95% CI:-0.03, 0.02; p = 0.720) or duration of follow-up (slope:-0.06; 95% CI:-0.37, 0.24; p = 0.681).
Conclusions: This meta-analysis suggests that Mg supplementation significantly reduces serum CRP level. RCTs with a larger sample size and a longer follow-up period should be considered for future investigations to give an unequivocal answer.
Reference:
Mazidi M, Rezaie P, Banach M. Effect of magnesium supplements on serum C-reactive protein: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Med Sci. 2018 Jun;14(4):707-716. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2018.75719. Epub 2018 May 11. Review. PubMed PMID: 30002686; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC6040119.
Keywords: magnesium supplements, serum C-reactive protein, systematic review and meta-analysis, randomised controlled trials (RCTs).
Join for free INPST as a member
The International Natural Product Sciences Taskforce (INPST) maintains up-to-date lists with conferences, grants and funding opportunities, jobs and open positions, and journal special issues with relevance for the area of phytochemistry and food chemistry, pharmacology, pharmacognosy research, and natural product science.