Yang Yang1, Dongdong Wang1, 2, 3*
Contribution participating in the INPST 2018 Science Communication Awards contest.
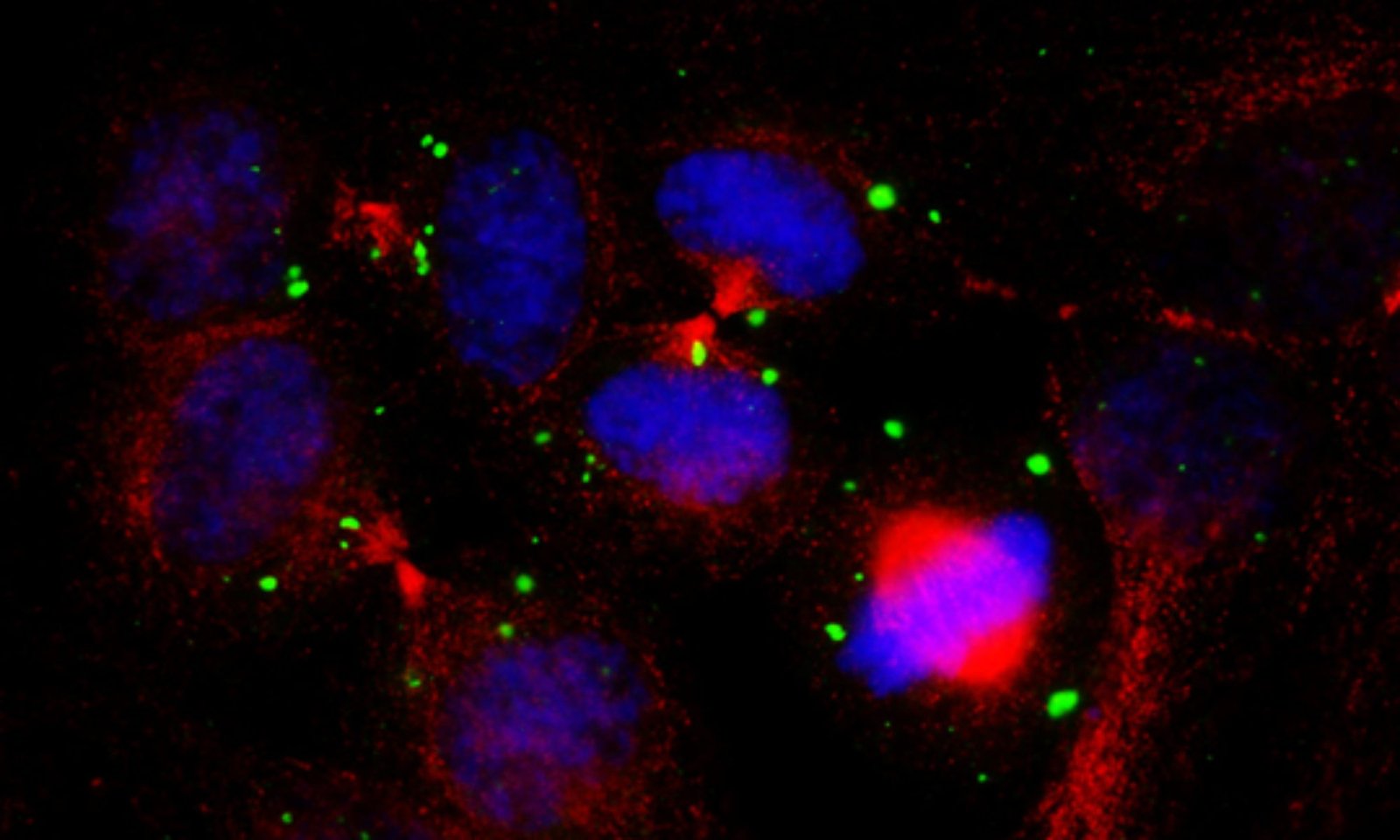
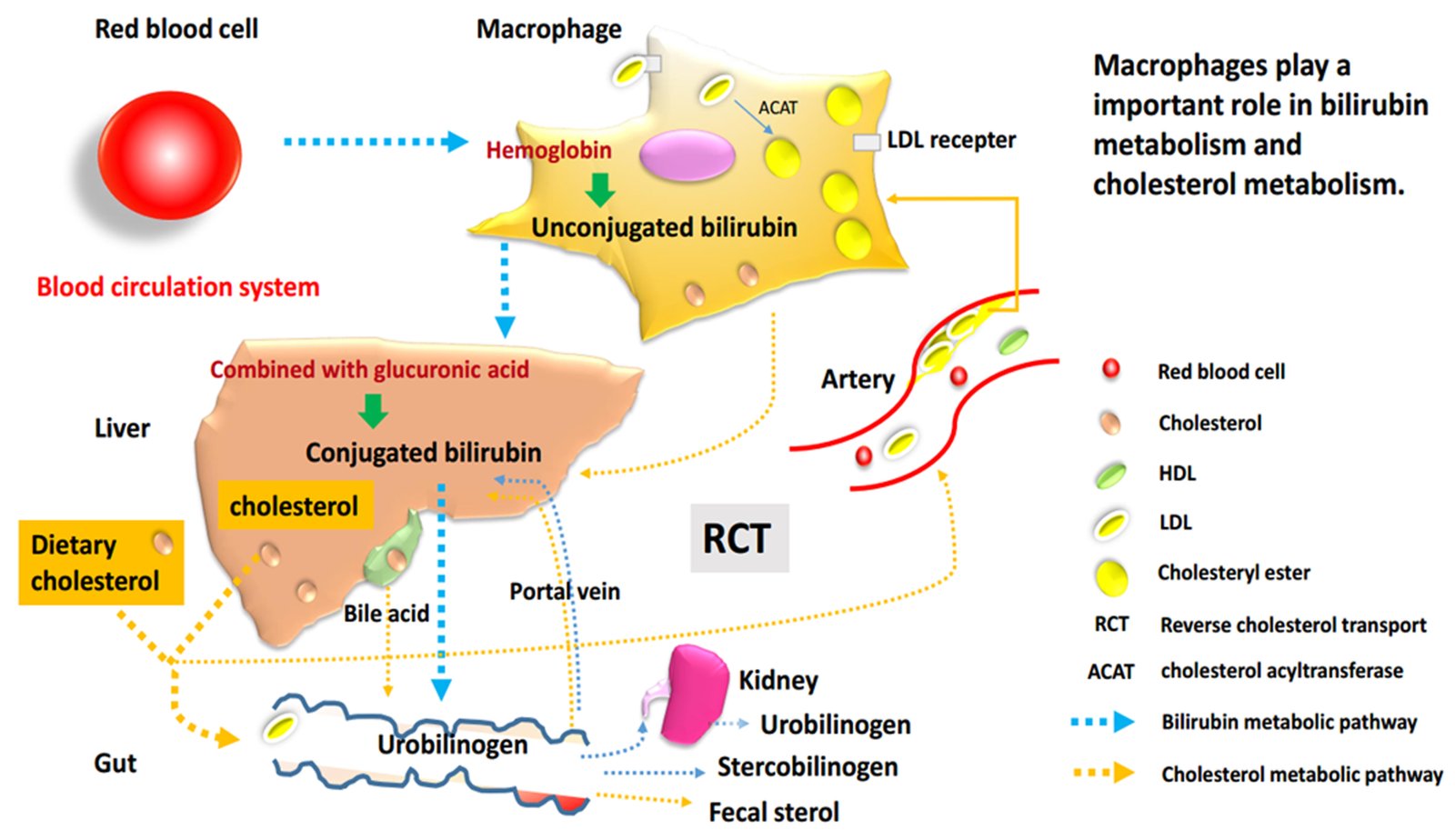
Bilirubin, a major pigment in bile with specific antioxidant properties, is a standard serum biomarker of liver function, which has particular toxicity due to irreversible damage to the brain and nervous system. Inexplicably, it is inversely correlated with cardiovascular disease risk. Our group found that unconjugated bilirubin (UCB) decreases macrophage cholesterol efflux and reduces the expression of ATP binding cassette A1 (ABCA1). These novel data underscore the complex bioactivity of bilirubin in the context of cardiovascular diseases (CVD) and may encourage further exploration of bilirubin’s effect on cholesterol metabolism and transport.
Continue reading “The complex bioactivity of bilirubin in the context of CVD”